- Published on
How I Build RPC Service For Web3 Project
- Authors

- Name
- Sunway
- @sunwayz365
Background
项目早期的RPC服务是以单节点+不同域名的方式部署的,用户需要在配置文件中配置多个 rpc 节点,以保证服务的可用性。
随着项目的发展,我决定为官方的 RPC 服务提供一个统一的访问入口,来提升服务的访问速度、稳定性以及可用性,同时降低用户配置的复杂度。
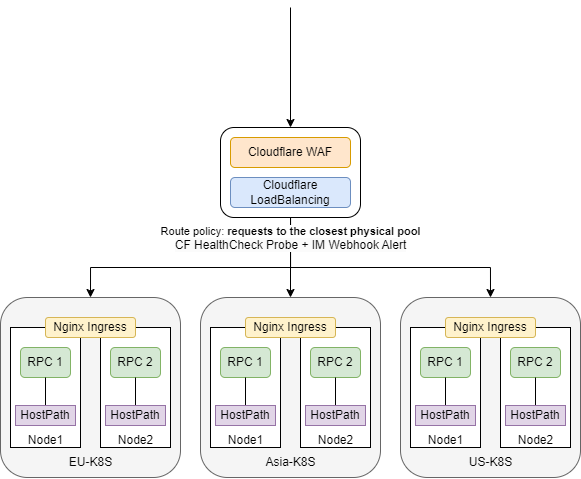
Architecture
nginx.conf
upstream nginx_ingress_http {
# nginx ingress svc type: NodePort
server 10.0.12.1:30080;
server 10.0.12.2:30080;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name rpc.example.com;
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/example.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/example.key;
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
location / {
proxy_pass http://nginx_ingress_http;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
}
ingress.yaml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: rpc-ingress
namespace: deapp
annotations:
nginx.org/websocket-services: rpc-svc
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
rules:
- host: rpc.example.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: rpc-svc
port:
number: 9944
service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: rpc-svc
namespace: deapp
spec:
sessionAffinity: ClientIP
sessionAffinityConfig:
clientIP:
timeoutSeconds: 3600
selector:
app: rpc
ports:
- protocol: TCP
name: websocket
port: 9944
targetPort: 9944
- protocol: TCP
name: metric
port: 9615
targetPort: 9615
- protocol: TCP
name: sync
port: 30336
targetPort: 30336
deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: rpc-deployment
namespace: deapp
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: rpc
app.kubernetes.io/component: rpc
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: rpc
app.kubernetes.io/component: rpc
spec:
containers:
- name: rpc-seattle
image: "cesslab/cess-chain:testnet"
imagePullPolicy: Always
command:
- "./cess-node"
- "--base-path"
- "/opt/cess/data"
- "--chain"
- "cess-testnet"
- "--port"
- "30336"
- "--name"
- "cess"
- "--rpc-port"
- "9944"
- "--execution"
- "WASM"
- "--wasm-execution"
- "compiled"
- "--in-peers"
- "75"
- "--out-peers"
- "75"
- "--state-pruning"
- "archive"
- "--rpc-max-connections"
- "65535"
- "--prometheus-external"
- "--rpc-external"
- "--rpc-cors"
- "all"
volumeMounts:
- name: rpc-storage
mountPath: /opt/cess/data
ports:
- containerPort: 9944
name: websocket
- containerPort: 9615
name: metric
- containerPort: 30336
name: svc
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /metrics
port: 9615
failureThreshold: 3
initialDelaySeconds: 60
periodSeconds: 300
volumes:
- name: rpc-storage
hostPath:
path: /app/data/rpc
affinity:
podAntiAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: app
operator: In
values:
- rpc
topologyKey: "kubernetes.io/hostname"
Problems
Problem 1: Failover Recovery
由于 CF Load Balancing 的 endpoint 是 k8s 集群的流量入口,而 CF Load Balancing 的 health check 无法对容器网络的 pod 进行健康检查,只能对暴露在公网的 nginx: 80/443 进行健康检查。
这就会导致一种情况:当集群内的 pod 出现故障而上层的 nginx 80/443 健康时,CF 仍然会错误地将流量转发至不可用的 pod,而不能实现自动降级;只有当被健康检查的对象 nginx: 80/443 出现异常时,才能实现流量降级。
这部分业务容器的告警功能只能自己另外实现。
Problem 2: Concurrency Limit
CF Load Balancing Free Edition 的 websocket 并发限制约为 40000,这部分测试结果对不同用户可能有些许差异。如果 RPC 服务的并发请求数超过这个限制,CF Load Balancing 会返回 503 Error,而且不会触发 Webhook Alert,所以至少升级 domain 至 pro edition 最好是 business edition。
Problem 3: Traffic Steering Policy
比如使用的路由策略是 Proximity Steering,一般来说最短路径会比较快,但也可能出现路由差的情况,比如日本用户根据 CF 的路由策略本该访问亚太的集群,当由于线路问题可能出现绕美的情况,从而导致请求变得更慢,购买Argo Smart Routing服务可能会有不错的性能提升。
再比如使用的路由策略是 Dynamic Steering,这个根据 CF 不同地域的健康检查探针的 latency 结果来路由,但这个 latency 只是针对健康检查探针所在地域来说的,并不一定是用户对源站的 latency,所以这个策略也不能提供最优的路由。
- Off: Cloudflare will route pools in failover order.
- Dynamic steering: Route traffic to the fastest pool based on measured latency from health checks.
- Geo steering: Route to specific pools based on the Cloudflare region serving the request.
- Proximity steering: Route requests to the closest physical pool.
- Random steering: Route to a healthy pool at random or weighted random.
- Least outstanding requests steering: Route traffic based on pool weights and number of pending requests.
Problem 4: Block Finalization Problem
分布式架构的 区块最终确认问题
背景知识:数据上链的过程包括广播(broadcast)和最终确认(finalize)等重要步骤。 创建的交易被发送到网络中的一个节点,该节点验证交易的格式和签名,如果验证通过,节点会交易转发给其他相连的节点,这个过程迅速重复,使交易在整个网络中传播。 然后网络中的共识矿工会根据自身的共识机制将数据打包出块;一旦一个区块被创建并通过共识,它会被广播到网络中的其他节点,然后其他节点验证这个新区块的有效性。 最终确认的时间因不同的区块链网络而异,比如BTC通常建议等待6个确认。
如架构图所示,3 个地域的 k8s 集群共 6 个 pod 实例。
Scenario: A当用户在浏览器端调用 RPC 方法创建一个 token 后,用户马上使用这个 token 去链上发起请求时可能出现 token invalid or token no exist 的问题,因为第2次请求可能路由到了不同的 rpc 实例,而由于区块没有同步,这个 token 还没有被区块打包同步到其他 rpc 实例,所以返回了 token invalid or no exist。这里可用通过 CF LoadBalancing Policy:Proximity steering 和 Kubernetes service sessionAffinity 解决。
当用户在浏览器端调用 RPC 方法创建一个 token 后,然后立刻使用这个 token 去向 DeApp server 发起请求,DeApp Server 去 verify token 的合法性时仍然可能出现 token invalid or token no exist 的问题,因为无法保证 DeApp Server 和用户浏览器请求的不是相同的k8s集群中的同一个rpc pod(实际上我们自己开发的Deapp使用的是内网的rpc,只允许集群内服务访问,公网的rpc只是备份节点),所以还是可能会出现请求失败的问题,甚至 DeApp Server 根本没有请求官方的 RPC,而是自己搭建了 RPC 供自己 DeApp 调用
当然还有其他的异常情况,比如可能是链本身交易失败的问题,但大部分还是因为区块未同步导致的 rpc 节点之间的数据不对称。最终的解决方案还是取决于链的出块时间,比如出块时间 6s,应用层再根据这个出块时间来做相应的调整
Problem 5: Backup policy
由于业务的特殊性,HPA/AutoScale 等功能在当前场景中可能无法很好地发挥作用。(这点可能和 k8s 弹性伸缩的特性相违背)
比如将 rpc pod replicas 从 2 扩容到 4, 实际上新的 rpc 实例是无法提供正常服务的,它是有状态的,无论存储是使用 csi/nfs storageClass 还是 hostPath 等等;因为新的 rpc 实例需要从 0 开始同步区块数据。
当链运行的越久,区块数量越多,需要同步的时间就越多,一般新的全节点实例需要至少等待 2~3 小时才能完成区块同步**(同步时间与链的运行时长成正比)**,之后才能正常提供服务。
所以,当节点需要扩容时,只能在 Cloudflare Load Balancing 上添加或者替换新的 endpoint,而不能直接扩容 k8s 集群中的 pod。
总结:当 k8s 集群宕机时,直接在 CF Load Balancing 上替换其他可用的 endpoint,当 k8s 集群恢复时,再变更 CF Load Balancing 的 endpoint 即可。
Problem 6: nginx reload
当集群租户变多,变更频率会增加,ingress 的创建变更会是个频繁事件,会导致网络经常不稳定。当k8s集群中服务发生变更时, nginx ingress 会触发 nginx reload,导致连接重置,所以不建议使用 nginx ingress,可以使用其他 ingress 或者 gateway
其他组件参考:
- https://github.com/Kong/kong
- https://github.com/alibaba/higress
- https://github.com/apache/apisix-ingress-controller
Advantage
这个架构的优点就是可以为跨地域的分布式服务提供一个统一的访问入口,以及优雅地实现不同地域流量调度
因为 CF Load Balancing 默认是被 Cloudflare 代理的,所以用户请求的流量首先会访问 Cloudflare, 在经过 Cloudflare 的 AntiDdos/Rules/WAF/LoadBalancing... 链路后,才会被转发到源站。
选择 Cloudflare Load Balancing 而非其他公有云 GTM 服务的原因:
1 全球网络覆盖: Cloudflare 拥有遍布 330 多个城市的数据中心网络,使得其负载均衡服务能够在全球范围内更快速、更高效地分发流量。
2 与CDN的无缝集成: Cloudflare 的负载均衡服务与其 CDN 服务紧密集成。
3 DDoS防护: Cloudflare 的负载均衡服务由其 DDoS 防护 DNS 支持。
4 多云和混合云支持: Cloudflare 的负载均衡服务可以跨多个云部署进行智能流量分配,包括私有云、公有云和混合云环境,而不局限于单一云提供商的生态系统。
5 成本效益: 由于 Cloudflare 的服务是作为统一平台的一部分提供的,一般会比单独购买和管理多个公有云提供商的 GTM 服务更具成本效益。
2024 December Latest Update
已老实,架构既然无法发挥 k8s 弹性扩展的作用,还有nginx ingress reload 这种恶心的问题,已放弃当前架构,改为了: CfLoadBalancing + (keepAlived + nginx) + systemd + logrotate + blackbox exporter + prometheus + grafana + alertManager